Introduction to 18th Century Art
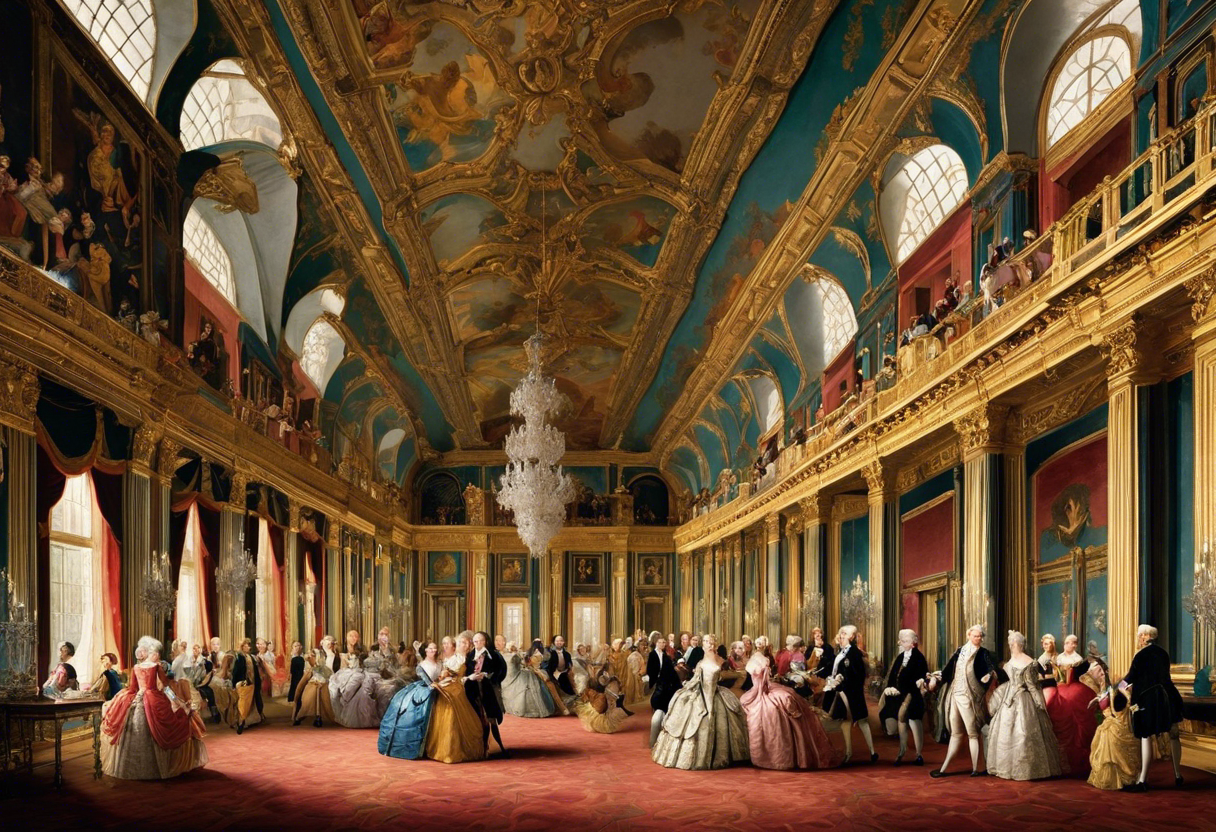

The 18th century was a period of great artistic development and experimentation in Europe. This century witnessed significant changes in art, marked by the transition from the grandeur of the Baroque era to the refinement of the Rococo style. It was a time when artists explored new subjects, techniques, and ideas, resulting in a diverse range of paintings that still captivate viewers today.
Historical Context
To understand 18th century art, it is important to consider the historical context in which it emerged. This period was characterized by political and social changes, such as the Age of Enlightenment and the rise of the Industrial Revolution. These societal shifts had a profound impact on art, leading to new interpretations of beauty, nature, and human emotion.
Neoclassicism and Romanticism
Two major artistic movements that dominated the 18th century were Neoclassicism and Romanticism. Neoclassicism drew inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman art, embracing ideals of rationality, order, and restraint. Artists sought to revive classical forms and subjects, often depicting heroic figures and historic events.
On the other hand, Romanticism celebrated individualism, emotion, and the sublime. Artists of this movement explored themes such as nature, folklore, and the supernatural. They sought to evoke powerful emotions in their viewers, creating atmospheric and dramatic compositions that evoked a sense of awe and wonder.
Key Artists and Works
The 18th century produced a multitude of talented artists whose works continue to be influential and appreciated. One such artist is Jean-Baptiste Greuze, a French painter known for his intimate and sentimental portrayals of everyday life. His works often depicted scenes of domesticity, innocence, and moral virtue.
Another notable artist from this period is Francisco Goya, a Spanish painter renowned for his powerful and often political artworks. Goya’s works explored themes of war, social injustice, and the human condition, illustrating the darker aspects of society with a raw and satirical style.
Finally, the paintings of Thomas Gainsborough, an English artist, captured the essence of the English countryside and its rural inhabitants. Known for his skillful depictions of landscapes and portraits, Gainsborough created atmospheric and evocative works that are admired for their naturalistic beauty.
Conclusion
The 18th century was a pivotal time in the history of art, witnessing a shift from the opulence of the Baroque era to the elegance of the Rococo and the exploration of new artistic movements such as Neoclassicism and Romanticism. The works of artists like Greuze, Goya, and Gainsborough exemplify the range and depth of artistic expression during this period. Whether capturing everyday life, provoking social commentary, or celebrating the beauty of nature, these paintings continue to captivate viewers and provide a window into the rich artistic heritage of the 18th century.
Key Characteristics of 18th Century Paintings
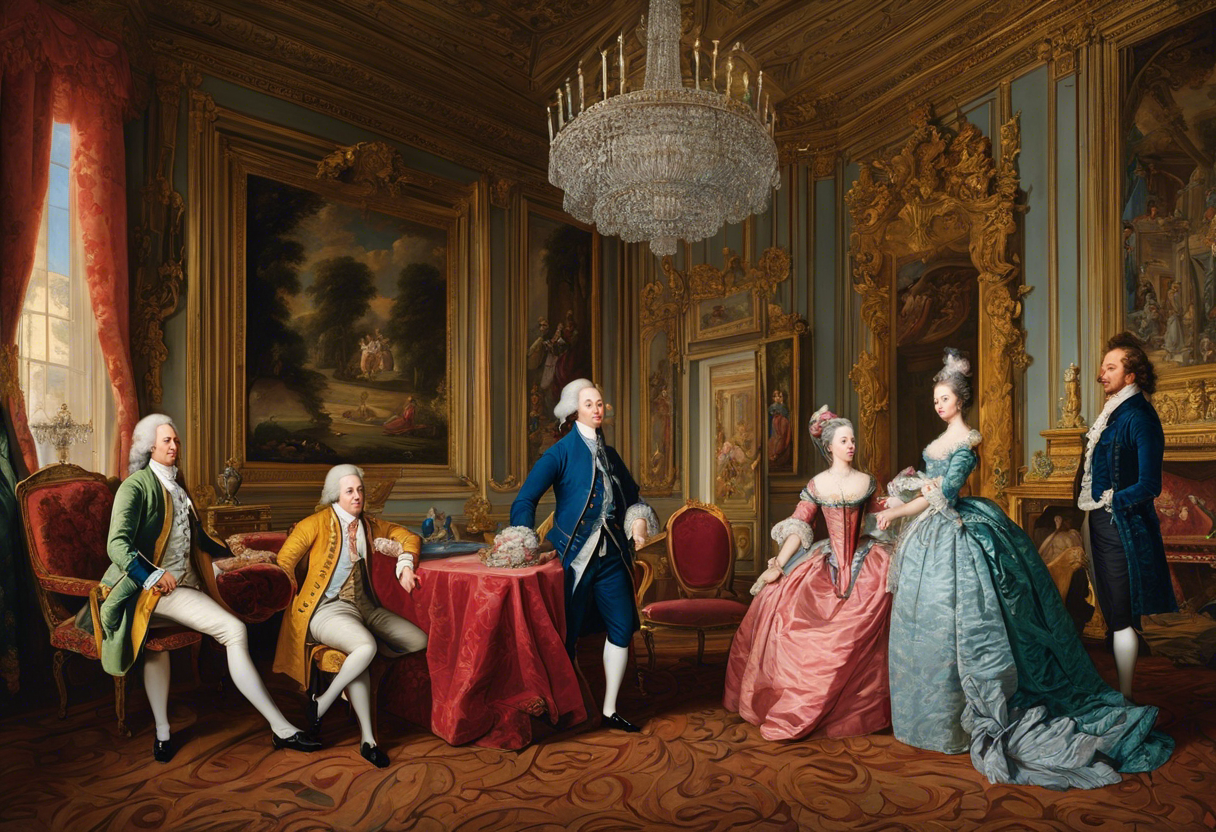

The 18th century was a period of great artistic expression, and paintings from this era have distinct characteristics that set them apart from other periods in art history. Here are some key characteristics of 18th century paintings:
1. Rococo Style
One of the most prominent styles of painting during the 18th century was the Rococo style. Rococo art was characterized by its elaborate and ornamental designs, with a focus on light colors, curved lines, and delicate details. The subject matter of Rococo paintings often revolved around themes of love, romance, and nature. This style was influenced by the aristocracy and was prevalent in France during the reign of King Louis XV.
2. Portraits and Landscapes
Portraiture was a popular genre in 18th century painting. Artists during this time sought to capture the personality and likeness of their subjects, often depicting them in luxurious settings to emphasize their status. Landscapes were also widely painted, with artists showcasing the beauty of nature and the picturesque countryside. These landscapes often depicted idyllic scenes with distant horizons, lush vegetation, and serene bodies of water.
3. Historical and Mythological Themes
Many 18th century paintings featured historical or mythological themes. Artists drew inspiration from classical mythology, biblical stories, and historical events to create narratives in their artwork. These paintings were often grand in scale and depicted scenes of heroism, religious significance, or events from history. Artists used these themes to convey moral, political, or social messages to their audience.
4. Neoclassical Influence
Towards the end of the 18th century, the Neoclassical style started to emerge, drawing inspiration from classical Greek and Roman art. Neoclassical paintings were characterized by their clear and precise lines, strong compositions, and a focus on moral and patriotic themes. Artists aimed to create artworks that portrayed noble virtues and promoted a sense of civic responsibility. Neoclassical artists sought to bring back a sense of order and reason through their art, in contrast to the lavishness of the Rococo style.
5. Use of Light and Color
Light and color played a significant role in 18th century paintings. Artists used light and shadows to create depth, enhance the three-dimensional effect, and emphasize certain elements of the composition. Color palettes varied depending on the style and subject matter, with Rococo paintings often featuring pastel tones and Neoclassical paintings employing a more restricted and muted color range. Artists carefully chose colors to create mood and evoke emotions in the viewer.
In summary, 18th century paintings were characterized by the Rococo and Neoclassical styles, the prevalence of portraits and landscapes, the use of historical and mythological themes, and the careful manipulation of light and color. These characteristics reflect the artistic trends and societal influences of the time, offering us a glimpse into the beauty and diversity of art in the 18th century.
Influential Artists of the 18th Century
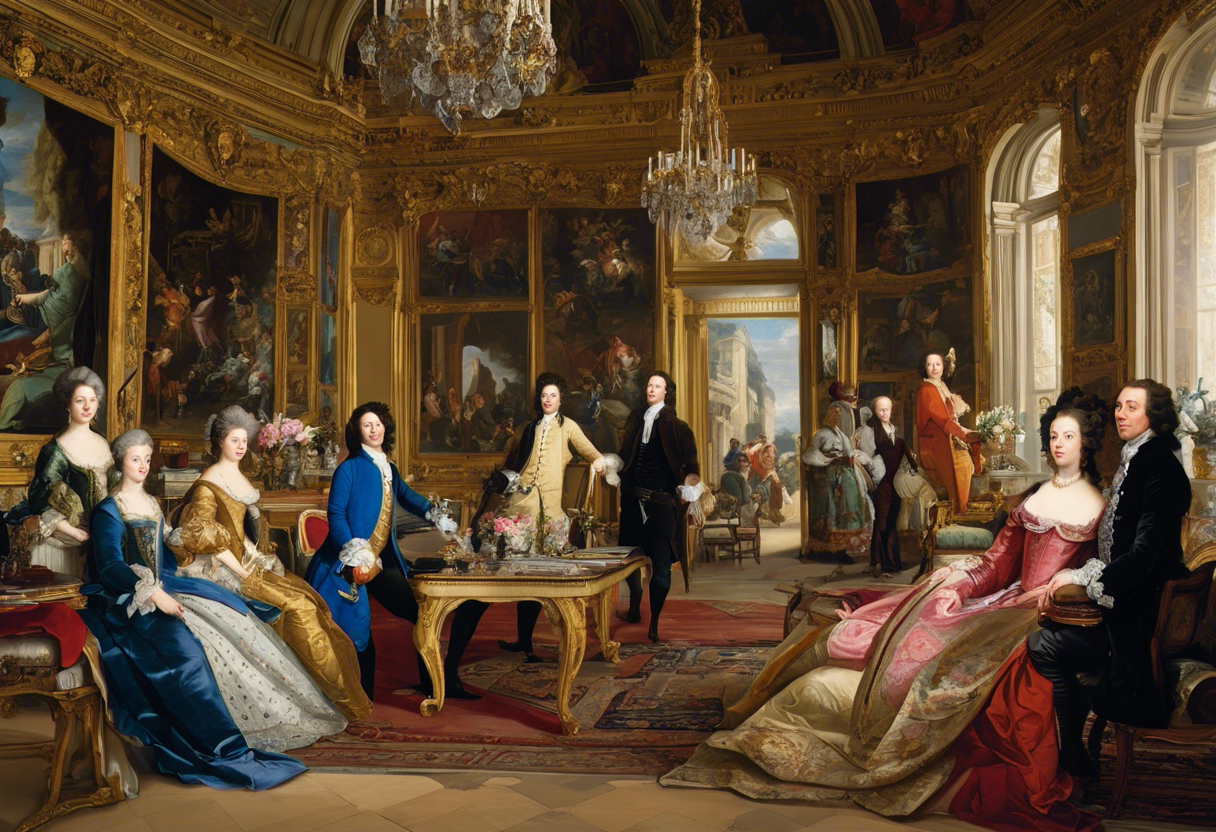

The 18th century witnessed the rise of several influential artists who made significant contributions to the world of art. These visionary individuals utilized their unique styles and techniques to create masterpieces that continue to captivate audiences to this day. Let us delve into the lives and works of some of these exceptional artists of the 18th century.
- Jean-Baptiste-Siméon Chardin – Chardin was a French painter known for his still-life and genre paintings. His meticulous attention to detail and realistic portrayal of everyday objects and scenes earned him great acclaim. Chardin’s works not only depicted ordinary subjects but also conveyed a sense of depth and emotion. His artistry laid the foundation for future generations of still-life painters.
- Thomas Gainsborough – Gainsborough, an English portrait and landscape painter, was renowned for his ability to capture the essence of his subjects. His portraits were often characterized by elegance and a keen sense of naturalism. Gainsborough’s landscapes, on the other hand, displayed a deep appreciation for nature’s beauty, with his brushstrokes recreating the tranquility of the countryside.
- Jean-Honoré Fragonard – Fragonard, a French Rococo painter, is celebrated for his delicate and sensuous depictions of romance and beauty. His paintings exude a whimsical charm and a joyful atmosphere, often featuring playful scenes of young lovers in idyllic settings. Fragonard’s vibrant use of colors and his ability to capture fleeting moments made him one of the most influential artists of his time.
- Sir Joshua Reynolds – Reynolds, an English portrait painter, was a prominent figure in the art world and the first president of the Royal Academy of Arts. His portraits were characterized by a sense of grandeur and elegance, often depicting individuals from the upper classes. Reynolds’ mastery of capturing likeness and his skillful use of light and shadow made him a highly sought-after artist.
- Jean-Baptiste Greuze – Greuze, a French artist, was known for his sentimental and moralizing portrayals of ordinary people. His paintings often depicted scenes of domestic life and showcased the virtues of modesty, virtue, and family values. Greuze’s works were highly popular during the 18th century and had a significant influence on the development of sentimental art.
These influential artists of the 18th century not only left a lasting impact on their contemporaries but also shaped the course of art history. Through their artistic abilities and innovative approaches, they brought new dimensions to various genres, from still-life painting to portraiture and romantic scenes. Their contributions continue to inspire and attract art enthusiasts, reminding us of the enduring beauty and expressive power of their works.
The Impact of 18th Century Art on Society
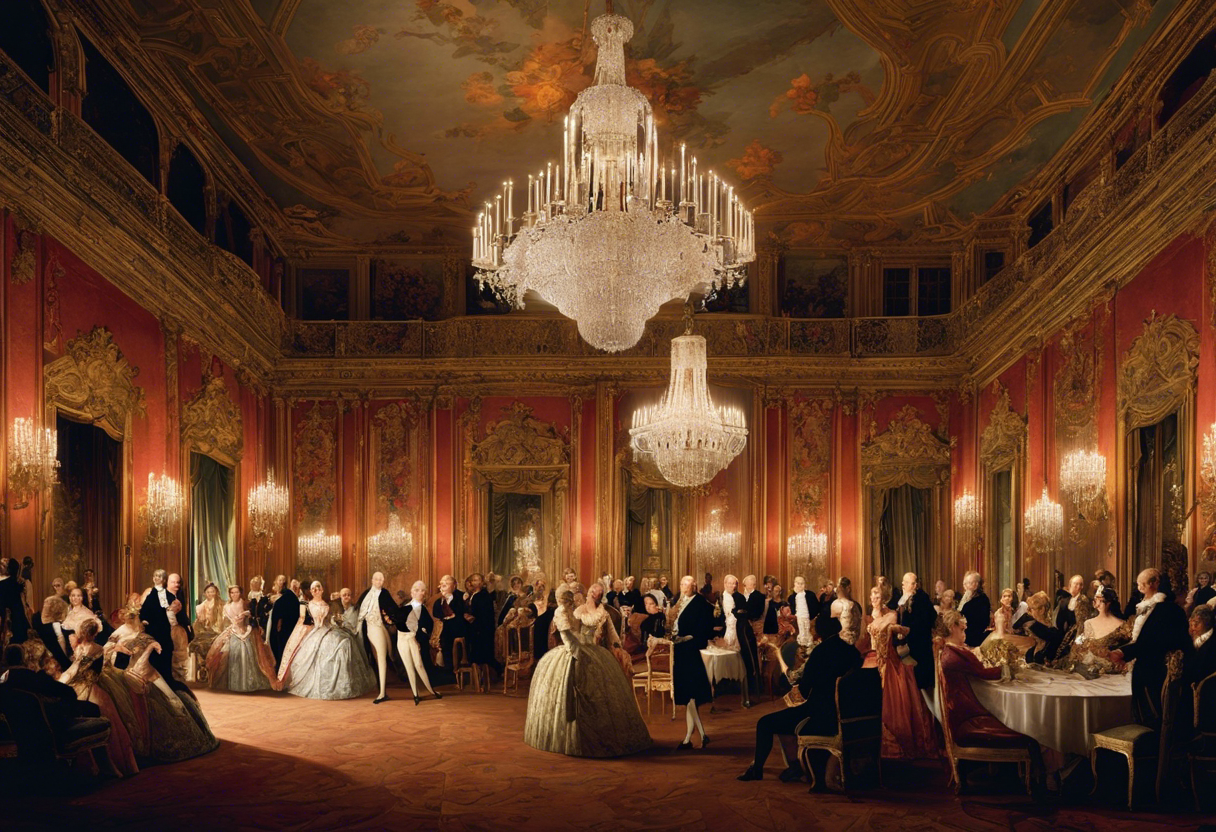

The art of the 18th century had a significant impact on society, shaping cultural trends, inspiring intellectual discourse, and reflecting the social and political climate of the time. Through various artistic movements and styles, artists of this era left an indelible mark on the art world and the society they lived in.
1. Influencing Cultural Trends
Art in the 18th century played a crucial role in shaping cultural trends. The Rococo style, known for its ornate and delicate designs, came to prominence during this period. It influenced not only painting but also architecture, furniture design, and fashion. The visually luxurious and extravagant style of Rococo art appealed to the aristocracy, who used it to display their wealth and position in society.
Additionally, the Neoclassical movement gained popularity during the 18th century, inspired by the revival of classical Greek and Roman art. This style emphasized simplicity, restraint, and the ideals of morality and virtue. Neoclassical artists aimed to elevate the intellect and promote rationalism, aligning with the Enlightenment philosophies of reason and logic.
2. Inspiring Intellectual Discourse
The art of the 18th century also inspired intellectual discourse and stimulated discussions about various political, social, and moral issues. Paintings often served as visual narratives addressing these topics. Artists depicted historical events, mythological stories, and scenes from everyday life, presenting them with symbolism and allegory to convey deeper meanings.
One prominent example is Jacques-Louis David’s painting, “The Death of Socrates,” which depicts the last moments of the Greek philosopher. This work sparked discussions about philosophy, morality, and the role of individuals in society.
3. Reflecting the Social and Political Climate
Artists of the 18th century used their works to reflect the social and political climate of the time. For example, during the French Revolution, artists became active participants in the political scene and created artworks supporting or criticizing the revolution.
The painting “Liberty Leading the People” by Eugène Delacroix is a prime example. It portrays the allegorical figure of Liberty guiding the people during the July Revolution of 1830. This painting exemplifies the artist’s political stance and his desire for liberty and justice.
Furthermore, portrait painting gained prominence during this era, bringing attention to influential figures in society. Portraits captured the likeness and personality of politicians, wealthy patrons, and cultural icons, shaping public perception and highlighting their significance in the social hierarchy.
The art of the 18th century not only reflected the social and political climate but also played a role in shaping public opinion and influencing societal values.
In conclusion, the impact of 18th-century art on society was profound and multi-faceted. It influenced cultural trends, inspired intellectual discourse, and reflected the social and political climate of the time. Artists of this era left a lasting legacy through their innovative styles, subject matter, and their ability to stimulate thought and engage with important societal issues. The art of this period provides us with valuable insights into the mindset and values of 18th-century society.
Exploring the Themes in 18th Century Paintings

The 18th century was a significant period in art history, witnessing the emergence of various distinct themes in paintings. Artists during this time were influenced by a range of factors, including the Enlightenment, the rise of the middle class, and the development of new artistic styles. Here, we will delve into some of the prominent themes that can be found in 18th century paintings.
- Portraits: Portraiture was a popular theme during the 18th century, reflecting the growing interest in individuals and their social status. Wealthy patrons commissioned portraits to showcase their wealth and power, often depicting themselves in elegant attire and sophisticated settings. Artists during this period were skilled at capturing the likeness and personality of their subjects, using techniques such as realistic representation and attention to detail.
- Landscapes: The 18th century saw a shift in the way landscapes were depicted in paintings. Rather than serving as mere backdrops for portraits or historical scenes, landscapes became the main subject of the artwork. Artists sought to capture the natural beauty of the world, often depicting idyllic scenes of countryside or exotic locations. These landscapes were often imbued with a sense of tranquility and harmony, highlighting the beauty of nature and the sublime.
- Historical and Mythological Scenes: Many 18th century painters turned to historical and mythological subjects for inspiration. These paintings often depicted pivotal moments from history or iconic myths and legends. Artists aimed to evoke a sense of grandeur and heroism through their artwork, often incorporating dramatic lighting and elaborate compositions. These paintings allowed viewers to connect with the past and reflect on the virtues and moral lessons portrayed in the scenes.
- Genre Scenes: Genre scenes, or everyday life scenes, gained popularity during the 18th century. These paintings depicted ordinary people going about their daily activities, capturing moments of leisure, work, or social interactions. Artists aimed to portray the diversity of social classes and human experiences, providing a glimpse into the realities of the time. Genre scenes often showcased vibrant colors, intricate details, and a sense of realism.
- Still Life: Still life paintings became increasingly popular during the 18th century. Artists excelled at capturing the beauty and intricacy of objects, often arranging them in carefully composed compositions. Still life paintings often included an assortment of fruits, flowers, food, and household items, sometimes with symbolic or allegorical meanings. These paintings showcased the artist’s technical skill in capturing textures, lighting, and the subtle variations in color.
In conclusion, 18th century paintings offer a rich tapestry of themes, reflecting the social, cultural, and artistic developments of the time. Whether it’s portraits, landscapes, historical scenes, genre scenes, or still life, these paintings tell stories, evoke emotions, and provide a window into the vibrant world of art in the 18th century.
The Evolution of Techniques in 18th Century Art

The 18th century was a time of significant evolution in the techniques used by artists. As art and culture underwent a transformation during this period, artists began to experiment with new materials and methods, leading to the development of unique styles and aesthetics.
- Oil painting: Oil painting continued to be the dominant technique used by artists in the 18th century. However, there were notable advancements in the way oil paints were prepared and applied. Artists started using a wider range of pigments, resulting in a greater variety of colors in their paintings. They also began to adopt a more meticulous approach to layering and glazing, creating a luminosity and depth that was characteristic of this period.
- Pastel: The 18th century saw the rise of pastel as a popular medium among artists. Pastels, made from powdered pigment mixed with a binder, offered a softer, more delicate effect, perfect for capturing the delicate nuances of portrait subjects and still-life compositions. Artists such as Jean-Baptiste Perronneau and Rosalba Carriera became known for their mastery of pastel techniques.
- Watercolor: Watercolor painting gained popularity in the 18th century, particularly in England. Artists like J.M.W. Turner and Thomas Gainsborough explored the possibilities of this medium, employing transparent washes and delicate brushwork to create atmospheric landscapes and detailed studies. Watercolor allowed for greater spontaneity and quick execution, making it ideal for outdoor sketching and capturing the fleeting beauty of nature.
- Engraving and etching: Printmaking techniques, such as engraving and etching, continued to be valued as means of reproducing and disseminating artworks. Artists like William Hogarth and Francisco Goya utilized these techniques to create powerful, narrative-driven prints that tackled social and political issues of the time. Engraving and etching allowed for precise detailing and intricate line work, making them well-suited to the meticulous nature of these artists’ works.
- Neoclassical style: The 18th century also witnessed the emergence of the neoclassical style, which sought inspiration from the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome. Artists like Jacques-Louis David embraced this style, employing sharp lines, precise anatomy, and a sense of idealized beauty in their works. Neoclassical artists often favored the use of oil painting techniques with a smooth finish, reminiscent of the marble sculptures of antiquity.
The techniques used in 18th century art reflected the changing aesthetics and cultural climate of the time. From the intricate glazes of oil paintings to the delicate strokes of pastels and watercolor, artists experimented with various mediums and styles to create artworks that captured the spirit of the era. These advancements in techniques laid the groundwork for further artistic innovations in the centuries that followed.
The Role of 18th Century Art in Artistic Movements

The 18th century was a period of dramatic change and innovation in the world of art. During this time, various artistic movements emerged, each with its own unique style and philosophy. These movements were heavily influenced by the art of the 18th century, which laid the foundation for many of the ideas and techniques that would shape the artistic landscape for centuries to come.
One of the significant influences of 18th century art was the rise of the Rococo style. Rococo art was characterized by its decorative and ornamental nature, with an emphasis on delicate details and pastel colors. This style emerged as a reaction against the formal and somber Baroque style that dominated the previous century. The Rococo movement had a profound impact on subsequent artistic movements, particularly in the realms of interior design, fashion, and decorative arts.
Another important development in 18th century art was the emergence of Neoclassicism. Inspired by the rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman art, Neoclassical artists sought to revive the ideals and techniques of the ancient world. This movement was fueled by a fascination with antiquity, a desire for moral and political reform, and a rejection of the excesses of the Rococo style. Neoclassical art laid the groundwork for the subsequent Romantic movement, which explored themes of emotion, nature, and individuality.
The Enlightenment, a period of intellectual and philosophical enlightenment that swept across Europe in the 18th century, also had a significant impact on artistic movements of the time. Artists began to use their work as a means of expressing their ideas and beliefs, challenging traditional norms and pushing the boundaries of artistic expression. This artistic rebellion against the status quo paved the way for future movements such as Realism and Impressionism, which sought to capture the world as it truly was and depict the fleeting impressions of light and color.
In addition to influencing subsequent artistic movements, 18th century art also played a crucial role in shaping the art market. The rise of art academies and salons in this period provided artists with a platform to exhibit their work and gain recognition. This increased visibility and networking opportunities helped to establish art as a legitimate and respected profession, elevating artists to the status of esteemed individuals in society.
In conclusion, the art of the 18th century had a profound impact on the development of artistic movements in subsequent centuries. From the ornate and decorative Rococo style to the revival of classical ideals in Neoclassicism, these movements set the stage for future artists to explore new techniques, ideas, and themes. The enlightenment and changing social attitudes of the time also played a significant role in shaping the direction of art and establishing it as a respected profession. By studying and appreciating the beauty of 18th century paintings, we gain a deeper understanding of the diverse and dynamic evolution of art throughout history. Comparing 18th Century Art with Other Periods
The 18th century was a period of great artistic diversity, marked by significant changes in artistic styles and themes. When comparing 18th century art with other periods, it becomes evident that each era produced unique artworks that reflected the social, political, and cultural contexts of the time.
- Renaissance Art:
The 18th century marked a departure from the highly detailed and religiously focused artworks of the Renaissance period. Renaissance art placed great emphasis on achieving realistic details, using techniques such as chiaroscuro and linear perspective. In contrast, 18th century art embraced a more Rococo style, characterized by its lightness, elegance, and delicate colors. The focus shifted from religious themes to daily life, landscapes, and portraiture.
- Baroque Art:
The 18th century saw a transition from the grandeur and drama of the Baroque period to a more refined and decorative style. Baroque art utilized dramatic lighting, dynamic compositions, and theatricality to evoke powerful emotions. In contrast, 18th century art adopted a more restrained and elegant approach. Artists like François Boucher and Jean-Antoine Watteau focused on creating delicate and whimsical scenes, often depicting the pleasures of courtly life and nature.
- Neoclassical Art:
Towards the end of the 18th century, a reaction against the decorative excesses of the Rococo style led to the emergence of Neoclassical art. Neoclassical artists aimed to revive the classical ideals of ancient Greece and Rome, drawing inspiration from mythology, history, and literature. Painters like Jacques-Louis David portrayed subjects with a sense of moral purpose, emphasizing the virtues of heroism and patriotism. Neoclassical art was characterized by its clean lines, classical proportions, and a focus on historical and allegorical themes.
- Romanticism:
In the early 19th century, the Romantic movement emerged as a reaction against the rationality and restraint of Neoclassicism. While not directly comparable to the 18th century, Romanticism shared some thematic elements with late 18th century art. Both periods celebrated nature, imagination, and the individual experience. However, Romantic art embraced a more emotional and expressive style, opening up new avenues for artistic exploration.
Overall, comparing 18th century art with other periods reveals the evolution of artistic styles, themes, and techniques over time. The 18th century marked a shift towards lighter, more decorative styles, as well as a greater emphasis on aspects of daily life and nature. Each period has its own unique characteristics and contributed to the rich tapestry of art history.
The Legacy of 18th Century Art in Modern Times
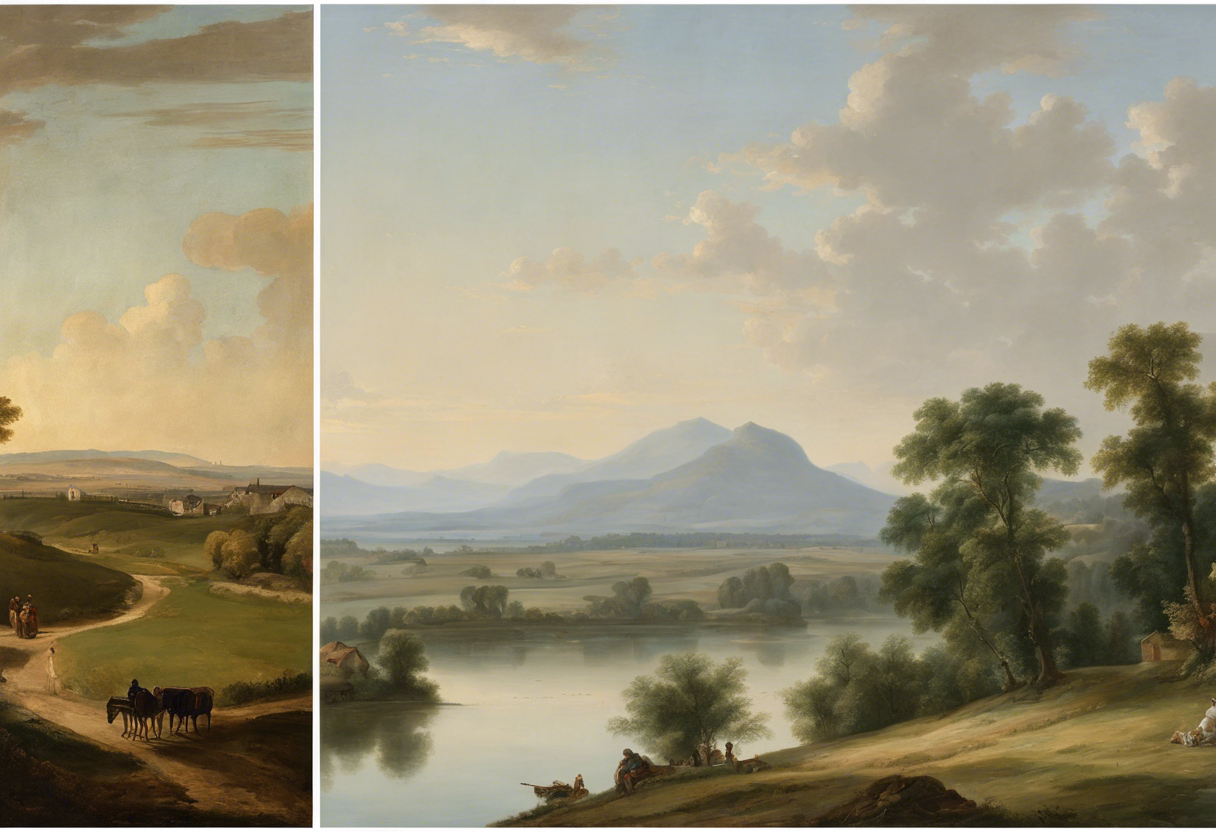
The art of the 18th century continues to have a profound impact on modern times, leaving behind a rich and enduring legacy. From the elegant portraits of the wealthy to the intricate landscapes and still lifes, 18th century paintings capture the essence of a dynamic era and continue to inspire and influence contemporary artists, collectors, and art enthusiasts alike.
One of the most significant contributions of 18th century art to modern times is its exploration of human emotion and the human experience. Artists of this period, such as Francisco Goya and William Hogarth, delved deep into the complexities of human nature, depicting a range of emotions and social realities in their works. Their ability to capture the essence of a moment and evoke strong emotions resonates with viewers even today.
The use of light and color in 18th century art has also left an indelible mark on modern painting. Artists like Jean-Baptiste-Simeon Chardin and Jean-Honoré Fragonard pioneered new techniques and approaches to the use of color and light, forging a path that would be followed by future generations. The vibrant and harmonious palettes used by these artists continue to inspire contemporary painters who seek to infuse their works with a sense of life and energy.
Another aspect of 18th century art that has endured through the centuries is the depiction of nature. Artists such as Thomas Gainsborough and Caspar David Friedrich captured the beauty and grandeur of the natural world in their landscapes, inspiring a sense of awe and appreciation for the environment. Their meticulous attention to detail and ability to convey a sense of serenity and tranquility in their paintings continue to resonate with modern audiences.
The social and political commentary found in 18th century art has also had a lasting impact on modern times. Artists like Jacques-Louis David and William Blake used their works to critique the social injustices and political upheavals of their time, reflecting the turbulent political climate of the era. Their bold and thought-provoking images continue to encourage dialogue and reflection on contemporary social and political issues.
In conclusion, the legacy of 18th century art in modern times is undeniable. Its exploration of human emotion, innovative use of light and color, depiction of nature, and social and political commentary continue to inspire and influence artists today. By appreciating and studying the beauty and significance of 18th century paintings, we gain a deeper understanding of our artistic heritage and the enduring power of visual expression.
Conclusion: Reflecting on the Importance of 18th Century Paintings

Throughout history, art has played a vital role in capturing the spirit of a particular era. This is particularly true when examining the captivating beauty of 18th century paintings. These artworks not only provide us with a glimpse into the past but also serve as a record of the societal, cultural, and artistic developments that occurred during this influential time period.
The importance of 18th century paintings lies in their ability to document the changing world around them. As the century progressed, so too did the art world, with new artistic movements and styles emerging. From the Rococo elegance of artists like Jean-Antoine Watteau to the grandeur of neoclassical masters such as Jacques-Louis David, each painting reflects the artistic ideals, values, and innovations of its time.
Moreover, 18th century paintings shed light on the social and cultural aspects of the era. These works often depict scenes of daily life, portraits of influential figures, or historical events, providing us with invaluable insights into the customs, fashions, and personalities of the period. Whether it be the lavish lifestyle of the aristocracy or the struggles of the working class, these paintings capture the essence of 18th century society.
Furthermore, the technical mastery exhibited in 18th century paintings cannot be overlooked. The delicate brushstrokes, realistic rendering of details, and skillful use of light and color demonstrate the talent and craftsmanship of the artists. These paintings serve as a testament to the dedication and expertise required to create such breathtaking works of art.
Beyond their historical and cultural significance, 18th century paintings also possess an inherent beauty that continues to captivate audiences today. The exquisite compositions, harmonious color palettes, and compelling narratives draw us into a world of elegance and drama. The emotional depth conveyed through each brushstroke evokes a range of feelings and resonates with viewers on a profound level.
In conclusion, exploring the beauty of 18th century paintings not only grants us a glimpse into the artistic achievements of the era but also provides us with a richer understanding of the social, cultural, and historical context in which these works were created. They remind us of the importance of art as a means of storytelling, as a reflection of society, and as a timeless source of inspiration. The legacy of 18th century paintings endures, allowing us to appreciate and learn from the remarkable artistry of the past.
