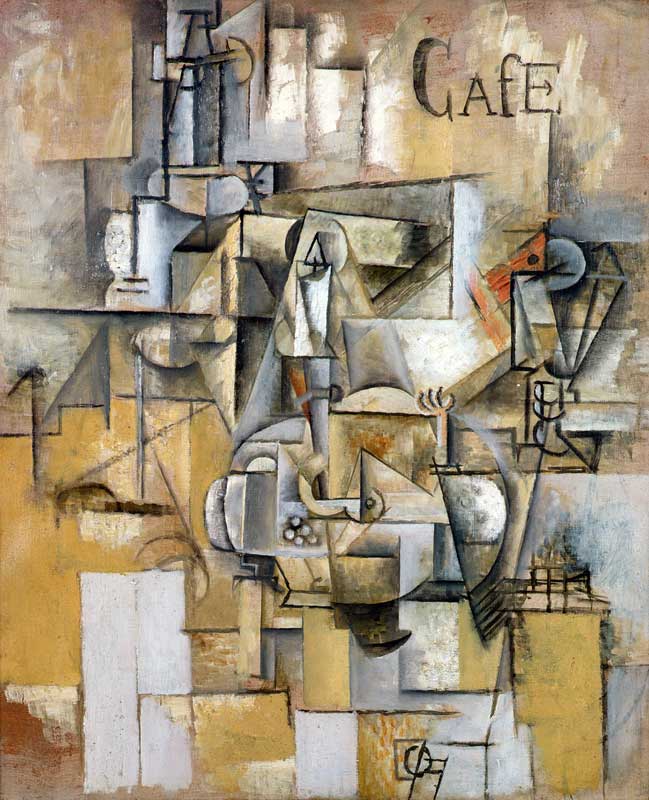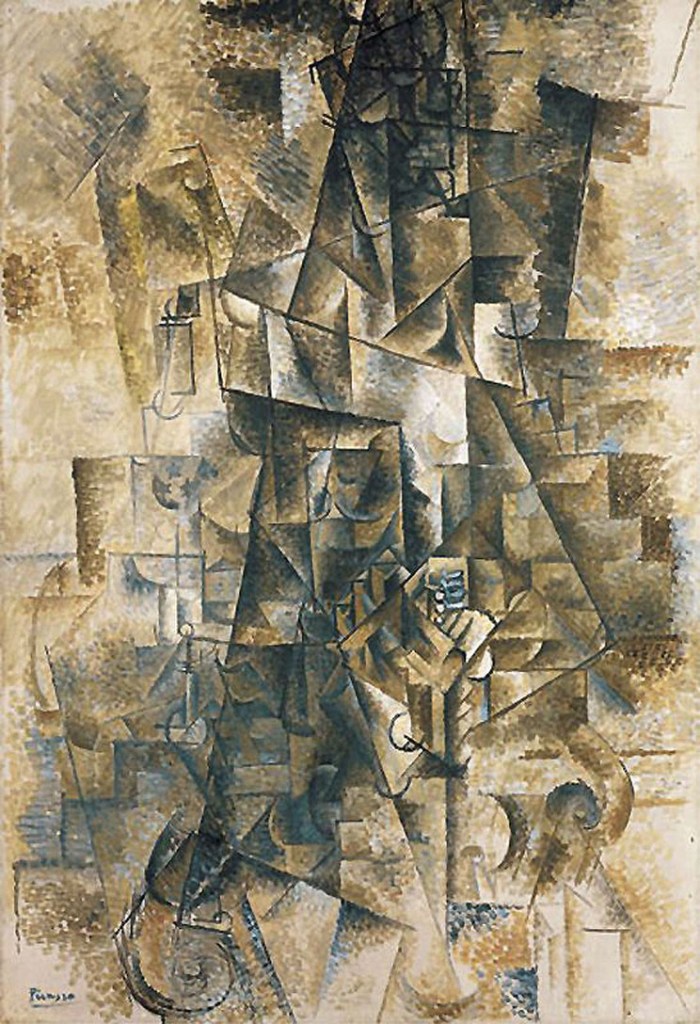Introduction to Cubism
Cubism is one of the most influential art movements of the 20th century, revolutionizing the world of visual arts. It emerged in the early 1900s, primarily in France, and challenged traditional perspectives and representations of reality. Developed by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, Cubism marked a significant departure from the established art forms of the time.
The Influences and Origins of Cubism
Cubism drew inspiration from various sources, including African and Iberian art, as well as the works of Paul Cézanne. Cézanne’s exploration of form, multiple viewpoints, and geometric simplifications laid the foundation for the development of Cubism. The artists involved in the movement sought to break down objects and subjects into their fundamental forms, allowing for a more analytical and abstract representation.
The Key Characteristics of Cubism
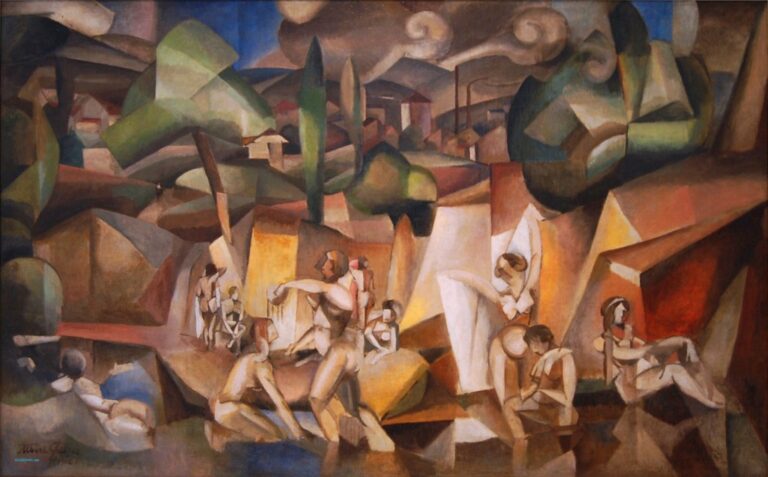
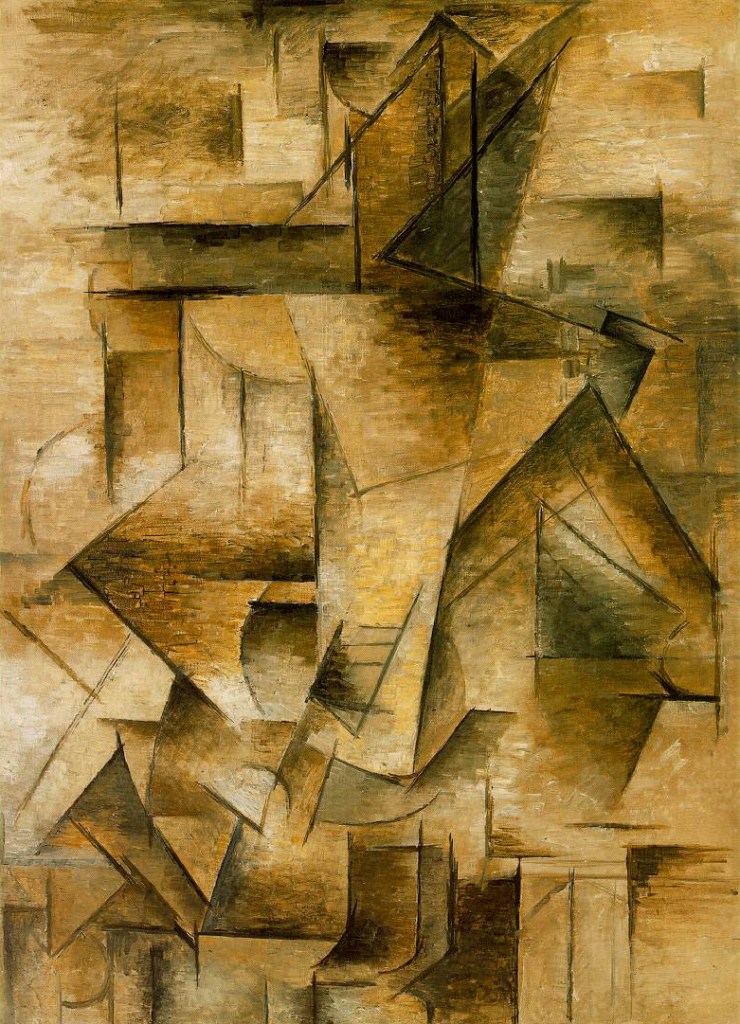
Cubism is characterized by its fragmented, geometric forms and the exploration of multiple viewpoints within a single composition. Rather than presenting a singular perspective, Cubist artists aimed to depict an object or subject from various angles simultaneously. This approach challenged the convention of representing a three-dimensional object on a two-dimensional canvas, leading to a new way of perceiving and interpreting art.
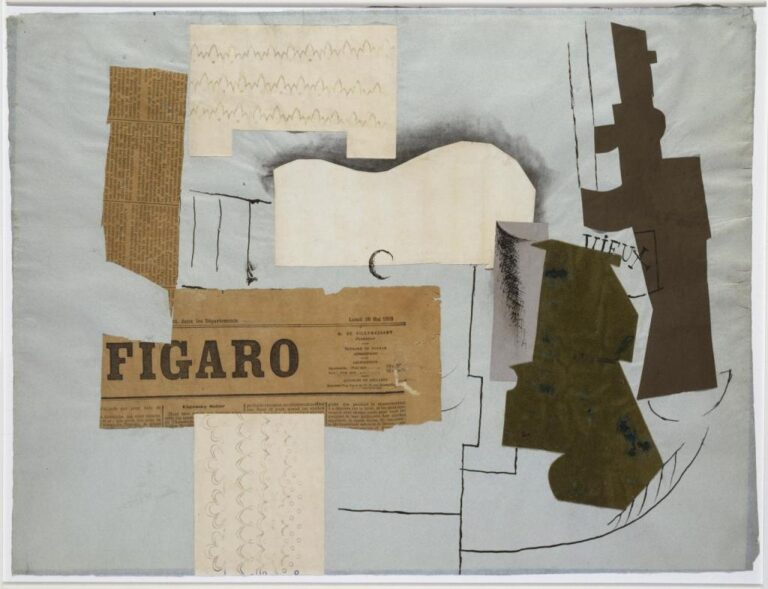
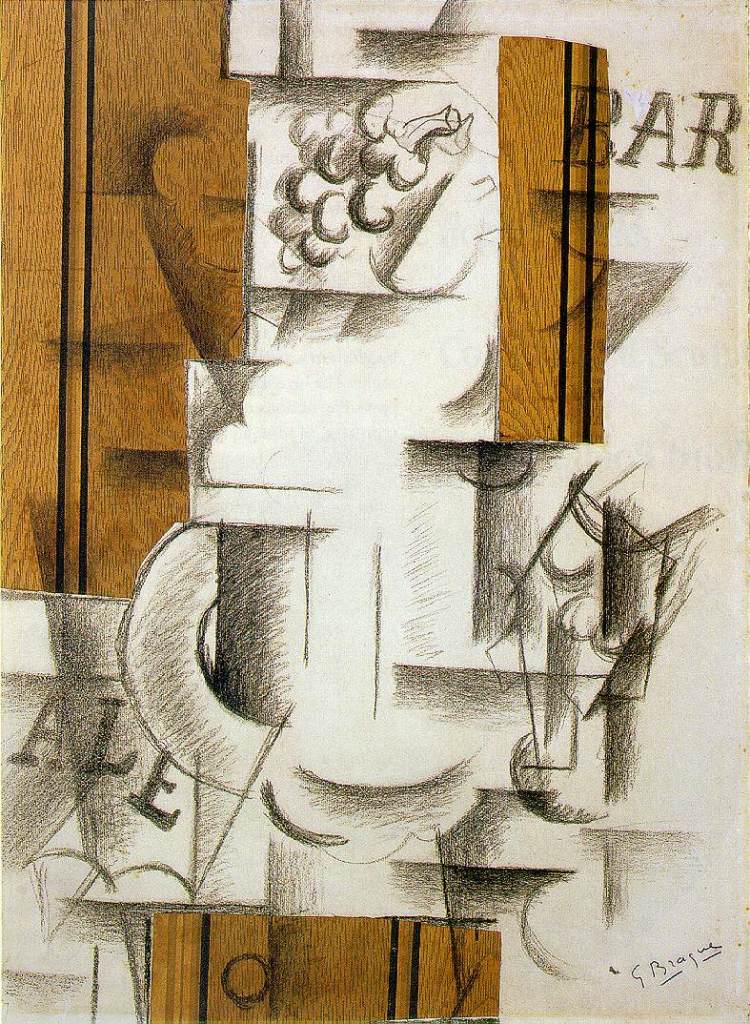
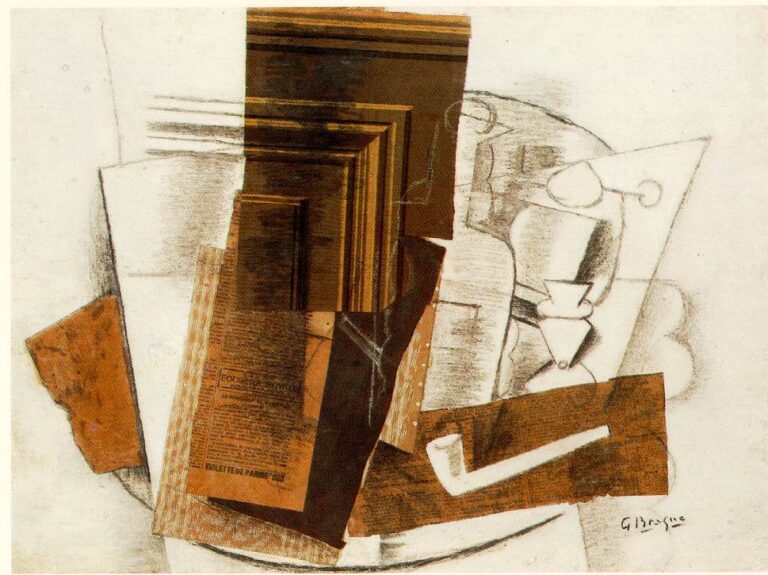
Another essential characteristic of Cubism is its emphasis on the concept of collage. Artists incorporated various materials, such as newspaper clippings and pieces of fabric, into their compositions, blurring the boundaries between art and everyday life.
The Major Artists of the Cubist Movement
Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque are considered the pioneers of Cubism, but numerous other artists contributed significantly to the movement. Some of the notable figures include Juan Gris, Fernand Léger, and Robert Delaunay.
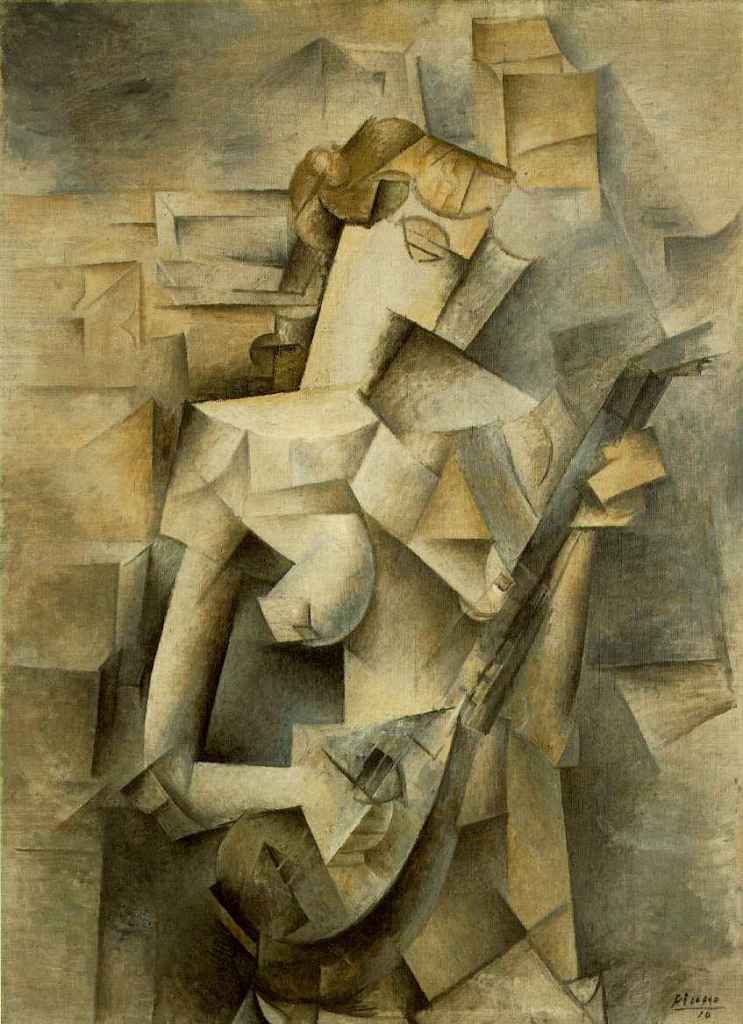
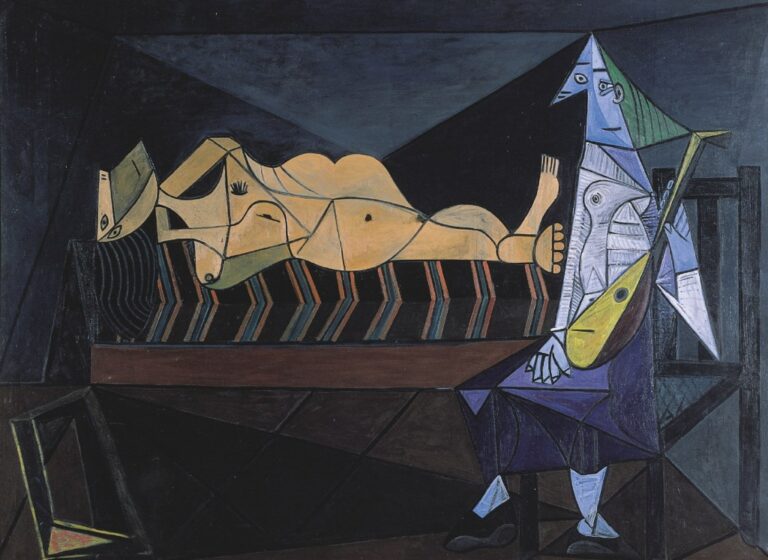
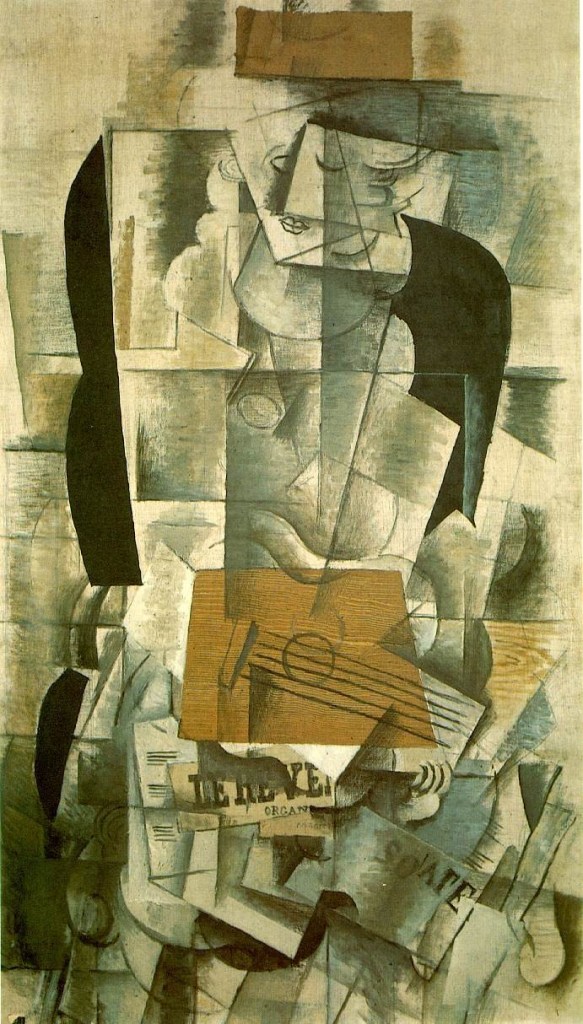
Picasso, known for his versatility and constant experimentation, played a pivotal role in the development and evolution of Cubism. His contributions to Analytical Cubism, characterized by its monochromatic palette and complex geometric forms, pushed the boundaries of artistic expression.
Braque, Picasso’s collaborator, developed what became known as Synthetic Cubism. He introduced collages and incorporated everyday objects into his compositions, further blurring the line between art and reality.
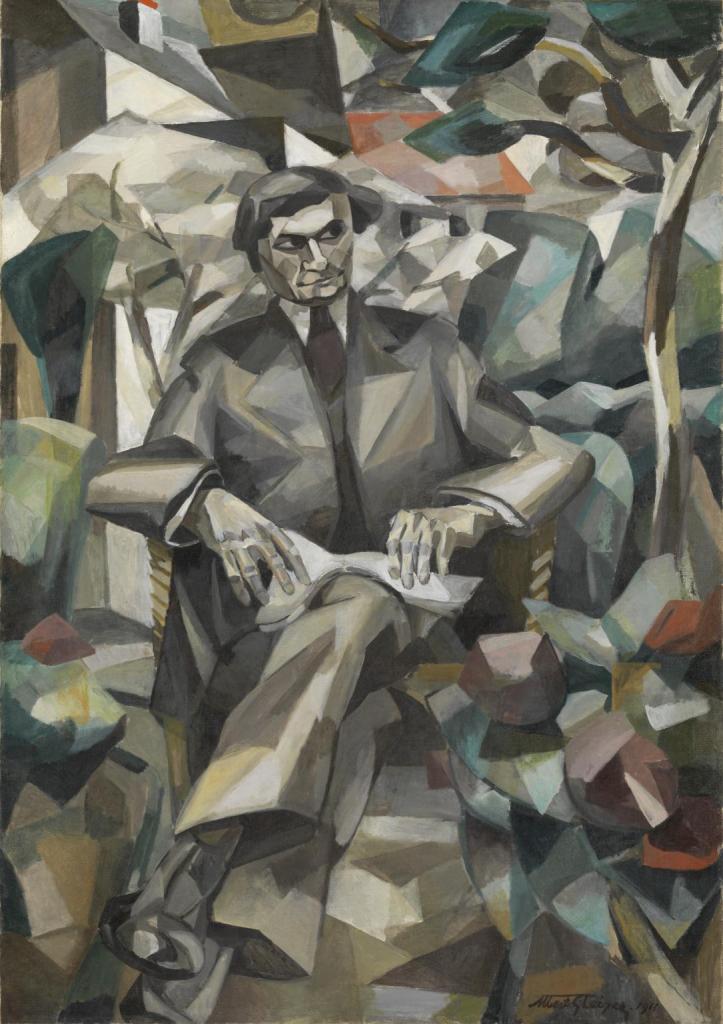
Juan Gris, influenced by both Picasso and Braque, brought a distinctive style to Cubism. His work featured a more refined and graphic approach, incorporating vibrant colors and intricate patterns.
Fernand Léger and Robert Delaunay explored the intersection between Cubism and other artistic movements, incorporating elements of Futurism and Orphism, respectively, into their work.
The Legacy and Impact of Cubism on Modern Art
Cubism revolutionized the art world and had a profound impact on subsequent art movements. Its influence can be seen in various styles and genres, from Abstract Expressionism to Pop Art.
By challenging traditional notions of representation, Cubism opened the door for artists to explore new ways of expressing their ideas and emotions. The movement encouraged a shift towards abstraction and pushed the boundaries of artistic expression.
Cubism also influenced the development of sculpture and architecture. Artists such as Constantin Brâncuși and Le Corbusier were inspired by the geometric forms and fragmented perspectives of Cubism, incorporating these elements into their own work.
Furthermore, Cubism paved the way for the exploration of multiple viewpoints and the deconstruction of form, leading to the emergence of other avant-garde movements such as Surrealism and Dadaism. Its legacy continues to resonate in contemporary art, as artists continue to push the boundaries of perception and representation.
In conclusion, Cubism remains a pioneering movement that revolutionized the art world. With its fragmented forms, multiple perspectives, and innovative use of materials, Cubism challenged traditional artistic conventions and paved the way for new modes of artistic expression. Its impact on modern art is undeniable, as it continues to influence and inspire artists to this day.